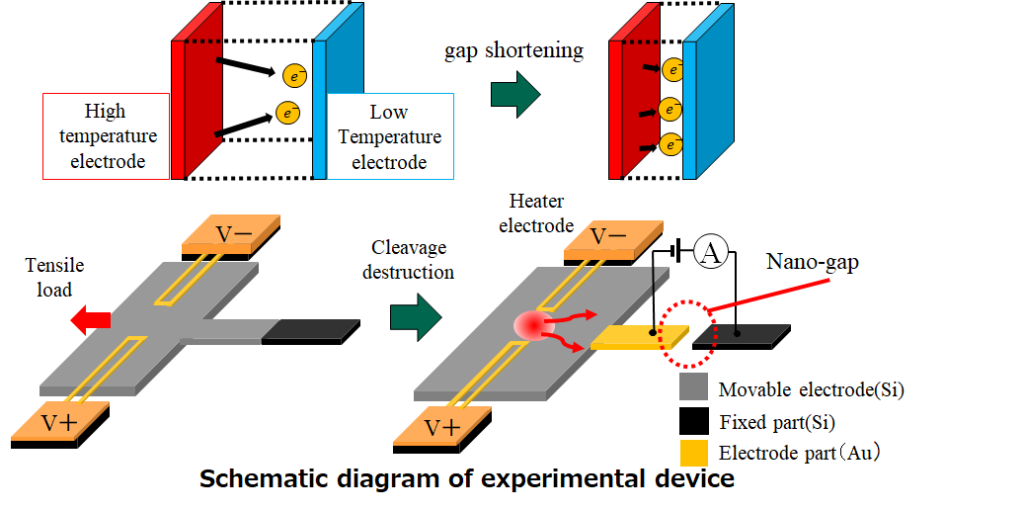
Temperature dependence of electron emission between cleavage planes for thermionic power generation
Thermionic power generation is a power generation method collects the emitted electrons by giving a temperature difference the electrodes. Normally, thermionic power generation requires a high temperature of 1000 ° C or more. However, by shortening the gap between the electrodes to nano size, electron emission between the electrodes is enhanced, and the applicable temperature range can be extended to around room temperature. However, there is no example that electricity was actually generated near room temperature.
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the temperature dependence of the electron emission between nano-gap fabricated by silicon cleavage fracture, and to verify the possibility of thermionic power generation near room temperature.
Thermionic power generation is a power generation method collects the emitted electrons by giving a temperature difference the electrodes. Normally, thermionic power generation requires a high temperature of 1000 ° C or more. However, by shortening the gap between the electrodes to nano size, electron emission between the electrodes is enhanced, and the applicable temperature range can be extended to around room temperature. However, there is no example that electricity was actually generated near room temperature.
Therefore, the purpose of this study is to evaluate the temperature dependence of the electron emission between nano-gap fabricated by silicon cleavage fracture, and to verify the possibility of thermionic power generation near room temperature.
[Applications] • Power supply for small autonomous sensor devices • Electron cooling device